Alternator: The Heartbeat Of Your Vehicle’s Electrical System
When you start your car and everything seems to power on—your lights, dashboard, AC, radio—it’s easy to forget about the small yet mighty device that makes it all possible: the alternator. Often taken for granted, the alternator is essential to keeping your vehicle’s electrical systems functioning and your battery charged. In this article, we’ll explore the significance of alternators, how they work, and why they’re indispensable to your vehicle’s operation.
Understanding the Alternator: What Is It and Why Does It Matter?
At its core, the alternator is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It’s responsible for recharging your car’s battery while the engine runs, ensuring that all of your vehicle’s electrical components remain powered. Without an alternator, your car battery would drain within a few hours, and your car wouldn’t be able to start. Essentially, the alternator keeps your battery from going flat while you’re on the go, ensuring smooth operations of vital systems such as lights, air conditioning, power steering, and more.
The Mechanism: How Does an Alternator Work?
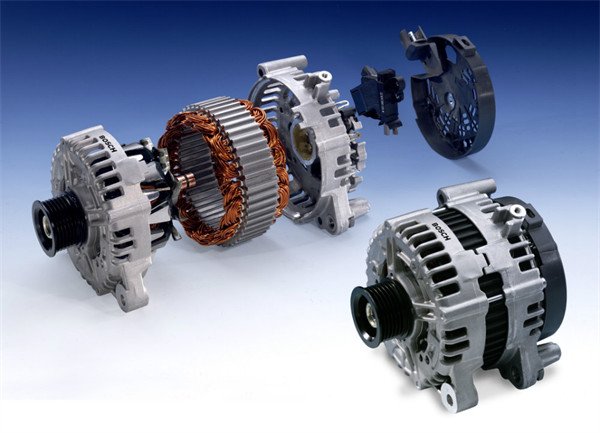
When you start your vehicle, the engine spins the alternator’s rotor, which is connected to a series of components like a stator and diodes. These parts work together to create alternating current (AC), which is then converted into direct current (DC) by the diodes. This DC current charges the car’s battery and powers the electrical systems.

- Rotor: The rotor is the rotating part of the alternator. It’s powered by the engine’s mechanical energy.
- Stator: Surrounding the rotor, the stator is made up of coils of wire. As the rotor spins, it induces an electric current in the stator.
- Rectifier: The AC current generated by the rotor is converted into DC by the rectifier, which is composed of diodes.
- Voltage Regulator: The regulator ensures that the alternator produces the right amount of voltage. If it produces too little, your battery will fail to charge; if it produces too much, it could damage electrical components.
Key Signs That Your Alternator Is Failing
Although alternators are built to last, they’re not invincible. Over time, they can wear out or encounter issues that affect their efficiency. Here are some signs that your alternator may be failing:
- Dashboard Warning Light: One of the most common indicators is the appearance of the “battery” or “alternator” warning light on your dashboard. This is your vehicle’s way of telling you that something might be wrong with the alternator or its charging system.
- Dimming or Flickering Lights: If your headlights or dashboard lights are dimming or flickering while driving, it could mean that the alternator isn’t generating enough power to keep them running.
- Strange Noises: A failing alternator can produce a whining or grinding noise, often due to worn-out bearings or a loose alternator belt. These noises can indicate mechanical issues with the alternator.
- Battery Issues: If your battery keeps dying, even after a jump start, it could point to an alternator problem. When the alternator isn’t charging the battery properly, the car may not hold a charge.
- Electrical Failures: If power windows, the air conditioning, or other electrical systems in your vehicle stop working correctly, the alternator might not be supplying enough energy.
The Importance of Regular Alternator Maintenance
Like all car components, alternators require routine maintenance to ensure longevity. Regular checks and maintenance are essential to prevent potential failures and avoid costly repairs. Here are a few ways to care for your alternator:
- Check the Alternator Belt: A loose or damaged alternator belt can cause inefficient charging. It’s essential to inspect the belt regularly and replace it if necessary.
- Inspect Wiring and Connections: Ensure that all wiring connections to the alternator are secure and free from corrosion. Loose or corroded connections can hinder the alternator’s performance.
- Monitor Battery Health: If you notice that your battery is draining quickly or not holding a charge, it could be due to the alternator’s inability to charge it properly. Regularly check your battery’s health alongside the alternator.
How to Extend the Life of Your Alternator
If you want to extend the lifespan of your alternator, here are a few tips:
- Avoid Short Trips: Short trips prevent the alternator from fully charging the battery. Long, highway trips allow the alternator to work more efficiently.
- Use Your Car Regularly: If you don’t drive your car often, the battery and alternator may not get the exercise they need. Try to take your car for a longer drive at least once a week.
- Turn Off Electrical Accessories: If you’re idling for an extended period, switch off lights, air conditioning, and other electrical accessories to ease the load on your alternator.
The Role of the Alternator in Modern Vehicles
In today’s modern cars, alternators have evolved with technology. Many newer models come equipped with high-output alternators to support the increasing demand for electricity. This is especially important with the rise of power-hungry features like infotainment systems, electric power steering, and adaptive headlights. As vehicles become more advanced, the alternator will continue to play a critical role in ensuring that all of these systems function properly.
Conclusion: A Small Part, But a Big Impact
The alternator may seem like a minor component in the grand scheme of your vehicle, but it plays a crucial role in keeping your car running smoothly. From ensuring your battery stays charged to powering essential electrical systems, the alternator is truly the heartbeat of your vehicle’s electrical system. Regular maintenance and timely repairs can go a long way in ensuring that this essential component remains in peak condition, allowing your car to perform at its best.
Alternator: The Heartbeat Of Your Vehicle’s Electrical System