The starter for car is one of the most crucial components of your vehicle, and understanding its role and functionality is essential for all car owners. Whether you are a seasoned driver or a novice, knowing how the car starter works can help you identify potential problems early, ensure smoother operation, and avoid breakdowns. In this article, we will delve into the importance of the starter for car, how it works, common issues, and why investing in a high-quality starter is a wise decision for any car owner.
What is a Starter for Car?
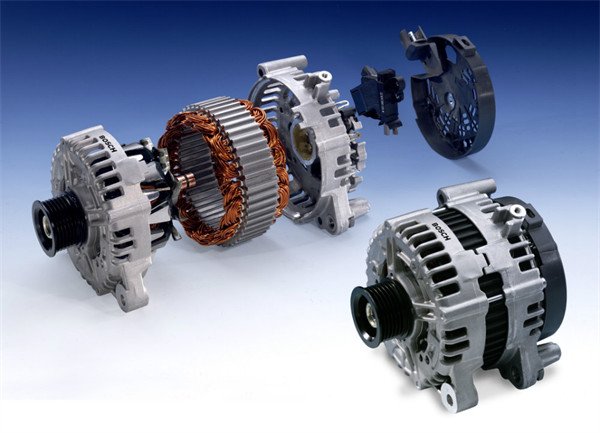
A starter for car is an electric motor that’s responsible for initiating the engine’s operation. In simple terms, the starter helps get your engine running by turning the flywheel, which then ignites the fuel and air mixture in the cylinders. When you turn the ignition key or press the “Start” button, the starter for car engages with the flywheel to turn the engine over, allowing it to start.
Without a properly functioning starter, your car would not start, regardless of how good the engine or other components are. The starter is, therefore, an integral part of your vehicle’s starting system. It’s typically located near the engine and connected to the battery.
The Role of the Starter for Car
The starter for car plays a critical role in ensuring that your engine starts and operates properly. Here’s a breakdown of the key functions of the starter:

1. Ignition Process
When you turn the ignition key, the starter for car receives an electrical signal from the battery. This initiates the motor, which in turn, engages with the flywheel. As the flywheel turns, the engine begins to crank, and the fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber ignites, starting the engine.
2. Engagement with the Flywheel
The starter for car is connected to the flywheel via a small gear known as the bendix drive. This drive pushes the starter motor’s gear to engage with the flywheel, allowing the motor to crank and start the engine. Once the engine starts, the gear disengages from the flywheel, and the starter motor stops.
3. Power Supply
The starter motor receives power directly from the car’s battery. This is why your car’s battery plays such a crucial role in the starting process. A weak or dead battery can lead to issues with the starter for car, as the motor may not have enough power to function.
How Does a Starter for Car Work?
Understanding how the starter for car works involves recognizing the steps that occur when you attempt to start your vehicle. Here’s a step-by-step look:
- Turn the Ignition Key or Press Start
When you turn the ignition key or press the “Start” button, the battery sends an electrical signal to the starter motor, activating it. - Starter Motor Engages the Flywheel
The starter for car motor then turns on and engages with the flywheel by moving a gear (called the Bendix drive). The motor cranks the engine, which begins to rotate. - Engine Cranks and Ignites
As the flywheel turns, the engine’s cylinders are activated, and a spark plug ignites the fuel-air mixture. This sparks the engine, causing it to start. - Disengagement
Once the engine is running, the starter motor’s gear disengages from the flywheel. The starter motor stops working, and the engine continues to run using its own power. - Battery Powers the Starter
Throughout this process, the car’s battery provides the necessary power to the starter motor, which is why a healthy, fully charged battery is essential for the system to work correctly.
Common Issues with Starter for Car
Like any other car part, the starter for car can face issues that may prevent it from working properly. Here are some of the most common problems:
1. Worn-Out Brushes and Components
Over time, the brushes and internal components of the starter motor can wear out due to constant use. This reduces the efficiency of the motor, and in some cases, the starter may fail to engage or turn the engine over.
2. Dead Battery
A weak or dead battery is one of the most common reasons a starter for car fails. If the battery doesn’t provide enough power, the starter motor won’t have the necessary current to turn the engine over. In this case, even if the starter is working properly, it won’t be able to start the vehicle.
3. Faulty Solenoid
The solenoid is an electrical component attached to the starter motor that helps engage the motor with the flywheel. A malfunctioning solenoid may prevent the starter from turning the engine over, leading to a no-start condition.
4. Broken or Damaged Starter Gear
If the Bendix drive or starter gear becomes damaged, the starter may fail to engage with the flywheel properly. This can result in the starter motor running without successfully turning the engine over.
5. Corroded Wiring or Connections
Corroded or loose wiring can also prevent the starter for car from receiving the correct electrical current from the battery. This could result in an intermittent start or no start at all.
6. Faulty Ignition Switch
If the ignition switch is faulty, it might not send the proper signal to the starter motor, preventing the engine from starting. This can be a challenging issue to diagnose because it may seem like a problem with the starter itself.
How to Know If Your Starter for Car is Failing
Recognizing the signs of a failing starter for car can help prevent you from being stranded or experiencing a breakdown. Here are some common symptoms:
1. Engine Won’t Crank or Start
If you turn the ignition key and the engine doesn’t crank or make any sound, it may be a sign that the starter motor is failing. The motor may not be able to engage the flywheel or may have a damaged internal component.
2. Clicking Sound
A clicking noise when you turn the key could indicate that the starter is trying to engage but isn’t able to. This could be caused by a dead battery or a faulty solenoid.
3. Grinding Noise
If you hear a grinding noise when starting the car, it could mean that the starter gear is not fully engaging with the flywheel or has become damaged. This requires immediate attention to avoid further damage.
4. Dashboard Lights Flickering
In some cases, flickering dashboard lights when you attempt to start your car can indicate issues with the starter motor. This might suggest that the motor is not receiving adequate power from the battery.
5. Intermittent Starting
If your car starts intermittently, the starter motor could be showing signs of wear. It may only engage properly once in a while, which will eventually lead to complete failure.
Maintaining Your Starter for Car
Proper maintenance can prolong the life of your starter for car and ensure reliable performance. Here are some tips to keep your starter in good condition:
- Regularly Check the Battery
The health of your battery is directly related to the performance of your starter. Make sure your battery is charged, clean, and free of corrosion. - Inspect Connections
Check the wiring and connections between the starter, battery, and solenoid for any signs of wear, corrosion, or loose connections. - Use Your Vehicle Regularly
If you don’t drive your car regularly, the starter motor may not get the necessary exercise to keep functioning well. Regular use helps keep all components, including the starter, in good shape. - Avoid Short Trips
Starting your car frequently without allowing it to run for an extended period can put undue strain on the starter motor. If possible, let your car run for a few minutes after starting it to allow the starter to disengage smoothly.
The starter for car is a small but vital part of your vehicle’s engine system. Without it, your car would not be able to start, no matter how well-maintained the engine is. Understanding the role of the starter, how it works, and recognizing early signs of failure can help you keep your vehicle running smoothly and prevent unexpected breakdowns.
Regular maintenance, prompt diagnosis of issues, and timely replacement of a faulty starter motor can ensure that your car continues to start reliably and efficiently. By investing in high-quality starters and staying on top of car care, you’ll enjoy the peace of mind knowing that your vehicle will always be ready to hit the road.