Starter Solenoid: The Unsung Hero Behind Your Engine’s Ignition Power
When you turn your car’s key or press the start button, a series of electrical components spring into action. One of the most critical—but often overlooked—parts in this process is the starter solenoid. Without it, your engine simply wouldn’t start. But what exactly is a starter solenoid, and how does it work? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down its function, components, signs of failure, and maintenance tips.
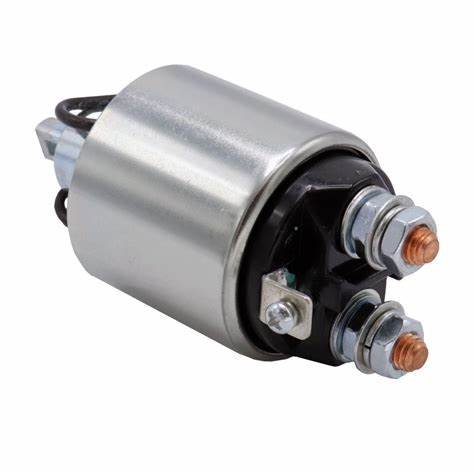

What Is a Starter Solenoid?
A starter solenoid is a small cylindrical device mounted on the starter motor. It acts as an electromagnetic switch that bridges the connection between the battery and the starter motor, enabling the engine to crank and start.
Key Components of a Starter Solenoid:
- Coil Windings: Generate the magnetic field needed for switching.
- Plunger: Moves to close the electrical circuit.
- Contacts: Complete the electrical path from the battery to the starter motor.
How Does a Starter Solenoid Work?
- Ignition Activation: Turning the key sends a small electrical current to the solenoid.
- Magnetic Field Generation: The current energizes the coil windings, creating a magnetic field.
- Plunger Movement: The magnetic field pulls the plunger, connecting the battery to the starter motor.
- Engine Cranking: The motor engages, turning the engine flywheel to start the car.
Why Is the Starter Solenoid Important?
- Crucial for Ignition: Without it, the battery’s power can’t reach the starter motor.
- Electrical Control: Prevents accidental engagement of the starter motor.
- Simplifies the Circuit: Reduces the need for high-current wiring throughout the vehicle.
Signs of a Failing Starter Solenoid
- Clicking Sound with No Start: Indicates the solenoid is receiving power but not connecting properly.
- Intermittent Starting Issues: Sometimes the engine starts, sometimes it doesn’t.
- No Sound at All: A completely failed solenoid or power issue.
- Smoke or Burning Smell: Indicates electrical arcing or overheating.
- Starter Motor Continuously Runs: A stuck solenoid can cause continuous engagement.
Common Causes of Starter Solenoid Failure
- Corrosion: On terminals or internal components.
- Worn Contacts: Over time, repeated use can degrade the contact points.
- Electrical Overload: Excess current can burn the internal coil.
- Heat Damage: Overheating due to prolonged cranking.
How to Test a Starter Solenoid
- Voltage Check: Use a multimeter to verify voltage from the battery.
- Continuity Test: Check for consistent circuit connection.
- Bench Testing: Remove and test the solenoid separately using a power source.
Maintenance Tips for a Reliable Starter Solenoid
- Clean Terminals: Prevent corrosion build-up.
- Secure Connections: Ensure cables are tight and secure.
- Avoid Excessive Cranking: Prolonged attempts to start the engine can damage the solenoid.
- Periodic Inspection: Check for wear during routine maintenance.
When to Replace a Starter Solenoid
- Persistent Starting Issues: If tests confirm failure.
- Visible Damage: Corrosion or burn marks.
- Old Age: Components degrade over time.
Conclusion
The starter solenoid is a small but vital component in your vehicle’s ignition system. Understanding how it works and recognizing signs of failure can help you avoid frustrating breakdowns. With proper maintenance and timely replacements, your starter solenoid will ensure your car starts smoothly for years to come
Starter Solenoid: The Unsung Hero Behind Your Engine’s Ignition Power